% Function that explains how to run dmdsp % % Written by Mihailo R. Jovanovic, September 2013 % % Notation: % % Matrices of snapshots % X0 = [x_0 ... x_{N-1}] % X1 = [x_1 ... x_N] % % Economy-size SVD of X0 % X0 = U*S*V' % % Inputs: matrices U'*X1, S, and V (for a specified flow type) % % Outputs: % % Fdmd - optimal matrix on the subspace spanned by the POD modes U of X0 % Edmd - eigenvalues of Fdmd % Ydmd - eigenvectors of Fdmd % xdmd - optimal vector of DMD amplitudes % answer - gamma-parameterized structure containing output of dmdsp function [Fdmd,Edmd,Ydmd,xdmd,answer] = run_dmdsp % Enter the flow type and the number of grid points for gamma prompt = {'1 (channel); 2 (screech); 3 (cylinder):',... 'Number of grid points for gamma:'}; name = 'Inputs for run_dmdsp'; numlines = [1 70]; defAns = {'1','200'}; opts.Resize = 'on'; opts.WindowStyle = 'normal'; opts.Interpreter = 'latex'; user = inputdlg(prompt,name,numlines,defAns,opts); flow_type = str2double(user{1}); gamma_grd = str2double(user{2}); % Load data for the specified flow type % Define sparsity-promoting parameter gamma if flow_type == 1, % Load data % Matrices U'*X1, S, and V % Sampling period dT % E-values of the Orr-Sommerfeld operator: Eos load channel/channel.mat % Sparsity-promoting parameter gamma % Lower and upper bounds relevant for this flow type gammaval = logspace(log10(0.15),log10(160),gamma_grd); elseif flow_type == 2, % Load data load screech/screech.mat % load matrices U'*X1, S, and V % Sparsity-promoting parameter gamma % Lower and upper bounds relevant for this flow type gammaval = logspace(log10(110),log10(33000),gamma_grd); elseif flow_type == 3, % Load data load cylinder/cylinder.mat % load matrices U'*X1, S, and V % Sparsity-promoting parameter gamma % Lower and upper bounds relevant for this flow type gammaval = logspace(1,log10(1600),gamma_grd); else error('Incorrect flow type') end % Matrix Vstar Vstar = V'; % The number of snapshots N = size(Vstar,2); % Optimal DMD matrix resulting from Schmid's 2010 algorithm % Fdmd = U'*X1*V*inv(S) Fdmd = (UstarX1*V)/S; % Determine the rank of Fdmd r = rank(Fdmd); % set the number of modes % E-value decomposition of Fdmd [Ydmd,Ddmd] = eig(Fdmd); Edmd = diag(Ddmd); % e-values of the discrete-time system % Form Vandermonde matrix Vand = zeros(r,N); zdmd = Edmd; for i = 1:N, Vand(:,i) = zdmd.^(i-1); end % Determine optimal vector of amplitudes xdmd % Objective: minimize the least-squares deviation between % the matrix of snapshots X0 and the linear combination of the dmd modes % Can be formulated as: % minimize || G - L*diag(xdmd)*R ||_F^2 L = Ydmd; R = Vand; G = S*Vstar; % Form matrix P, vector q, and scalar s % J = x'*P*x - q'*x - x'*q + s % x - optimization variable (i.e., the unknown vector of amplitudes) P = (L'*L).*conj(R*R'); q = conj(diag(R*G'*L)); s = trace(G'*G); % Cholesky factorization of P Pl = chol(P,'lower'); % Optimal vector of amplitudes xdmd xdmd = (Pl')\(Pl\q); % Sparsity-promoting algorithm starts here % Set options for dmdsp options = struct('rho',1,'maxiter',10000,'eps_abs',1.e-6,'eps_rel',1.e-4); % Call dmdsp % % Inputs: (1) matrix P % vector q % scalar s % sparsity promoting parameter gamma % % (2) options % % options.rho - augmented Lagrangian parameter rho % options.maxiter - maximum number of ADMM iterations % options.eps_abs - absolute tolerance % options.eps_rel - relative tolerance % % Output: answer - gamma-parameterized structure containing % % answer.gamma - sparsity-promoting parameter gamma % answer.xsp - vector of amplitudes resulting from (SP) % answer.xpol - vector of amplitudes resulting from (POL) % answer.Jsp - J resulting from (SP) % answer.Jpol - J resulting from (POL) % answer.Nz - number of nonzero elements of x % answer.Ploss - optimal performance loss 100*sqrt(J(xpol)/J(0)) tic answer = dmdsp(P,q,s,gammaval,options); toc
Description of run_dmdsp.m
>> [Fdmd,Edmd,Ydmd,xdmd,answer] = run_dmdsp;
Matlab function run_dmdsp.m allows users to:
run standard DMD algorithm;
call dmdsp.m.
When prompted to select the flow type, please choose:
1 – for channel flow;
2 – for screeching jet;
3 – for cylinder bundle.
You will also be prompted to enter a desired number of grid points for
the spatially-promoting parameter 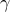 ; the default value is set to
200. These points are logarithmically spaced between minimal and maximal
values that are well-suited for the three examples presented in our
paper and on this website.
; the default value is set to
200. These points are logarithmically spaced between minimal and maximal
values that are well-suited for the three examples presented in our
paper and on this website.
run_dmdsp.m will then upload data necessary for conducting DMD and DMDSP and return:
Fdmd – optimal matrix on the subspace spanned by the POD modes
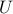 of
of 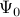 ;
;Edmd – eigenvalues of
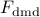 ;
;Ydmd – eigenvectors of
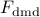 ;
;xdmd – optimal vector of DMD amplitudes;
answer –
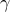 -parameterized structure containing the output of dmdsp.m.
-parameterized structure containing the output of dmdsp.m.